
Best Seed Banks Shipping To The USA
Buying cannabis seeds is a minefield. Finding a reliable seed bank that ships to you, has a good price and can take a card payment is far too difficult. That’s […]
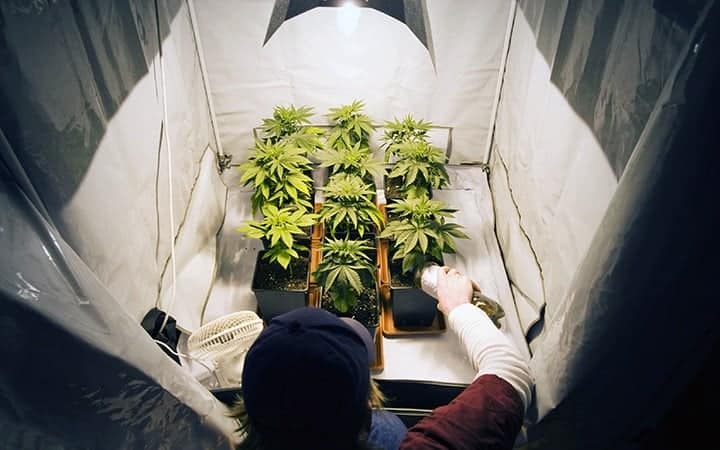

8 Steps To Growing Cannabis Indoors
Growing weed is easy but growing top-shelf cannabis is a skill. Beginner growers may seem overwhelmed by the long list of fundamentals that a grower must abide by, so below […]
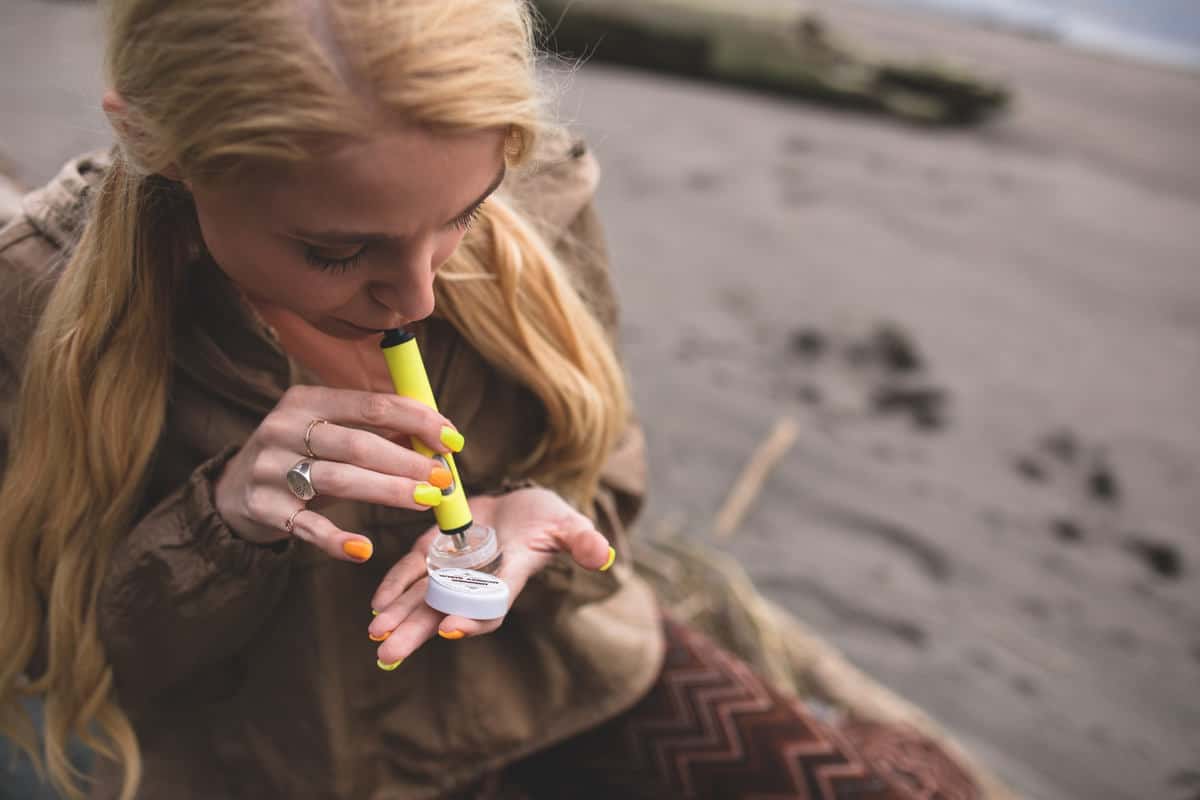

How Much is a Dab Pen?
When it comes to using cannabis on the go, dab pens offer a wonderfully convenient way to get an intense hit wherever you are. Whether you’re new to dabbing or […]

Buying Cannabis Seeds to Ship to the US
Buying and shipping cannabis seeds to the US can be challenging due to complex legal restrictions, varied purchasing options and complicated shipping arrangements. However, if it’s done correctly can provide […]
How Much Do Bongs Cost?
Bongs have been a popular way to smoke cannabis for decades, offering a smooth and cool smoking experience that many cannabis enthusiasts enjoy. If you’re looking to buy a new […]
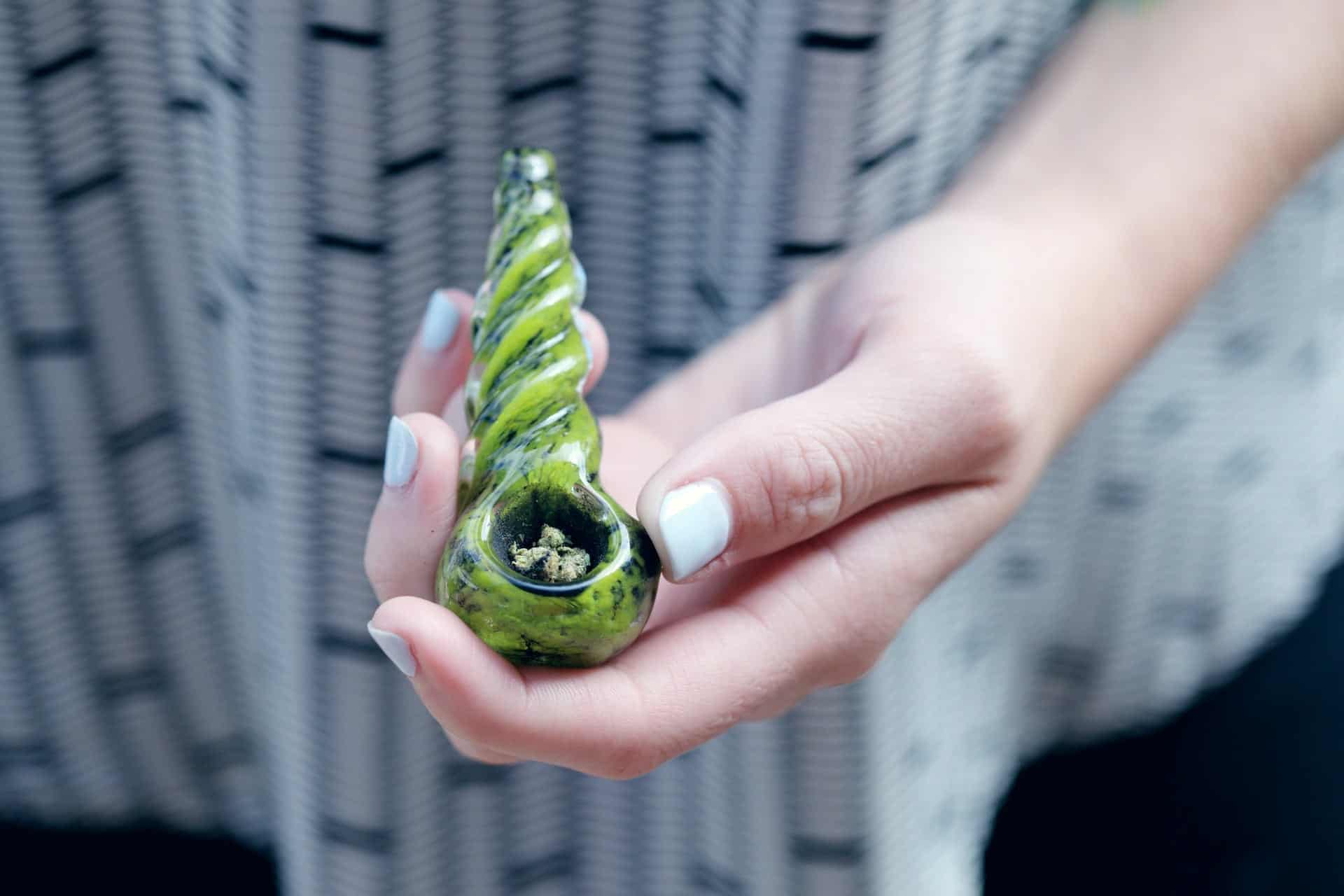

How Much Does a Weed Bowl Cost?
One of the simplest ways to smoke weed is with a bowl; a weed bowl is a short, portable pipe with a large bowl and thick stem. The open bowl […]
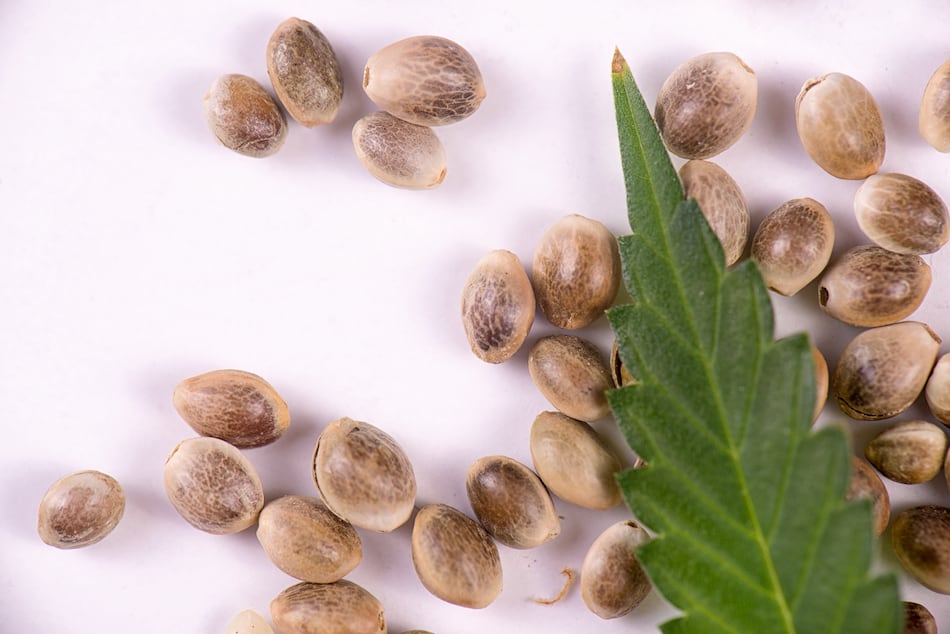

How Much Do Cannabis Seeds Cost?
With more and more people learning about the benefits and enjoyment that can come from cannabis use it’s no surprise that the interest in cannabis seeds has also grown. Before […]

9 Ways to Save Money on Weed
Despite legalization in some parts of the world, smoking or vaping weed can still be an expensive habit. However, with a little patience and some careful research, there are lots […]

Best Online Weed Dispensary Canada
With more and more online weed dispensaries offering delivery throughout Canada, it can be hard to determine which are legit and which will leave you with empty pockets. At Cannabis […]

A Sawbuck of Weed: What is it?
It’s green, it’s sticky, and it’s worth $10. What is it? A sawbuck of weed! The term sawbuck is probably something you have encountered when making a purchase, but what […]

Cannabis Seed Banks That Accept PayPal
When making any purchase online, PayPal is often the most convenient way to send your money. It offers payment protection, password-protected access, no need to enter long card numbers and […]
420 Seeds Review
420 Seeds Information Initially founded in 1999, 420 Seeds aim is: ‘To deliver the world’s finest genetics to your door, every time.’ To achieve this, they use decades of expertise […]